 Genre/Topic: Prepositions
Genre/Topic: Prepositions
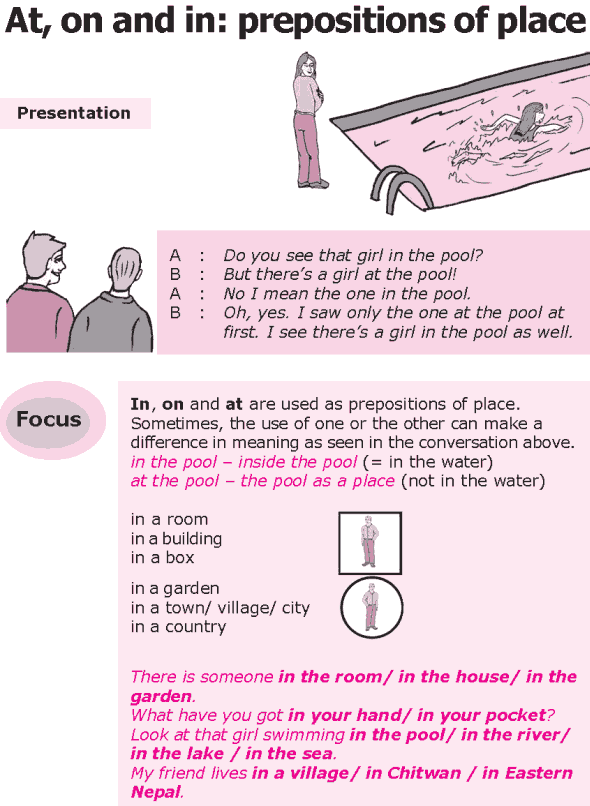
What is the difference between ‘in’ and ‘at’? What is the difference between ‘in’ and ‘on’? What is the difference between ‘at’ and ‘on’?
 Genre/Topic: Prepositions, Verbs
Genre/Topic: Prepositions, Verbs
What is the difference between ‘agree with’, ‘agree about’ and ‘agree to’? What is the difference between ‘care for’ and ‘care about’? Are ‘shout at’ and ‘shout to’ used for the same purposes? What is the difference between ‘point at’ and ‘point to’? What is the difference between ‘throw something at’ and ‘throw something to’? […]
 Genre/Topic: Prepositions
Genre/Topic: Prepositions
When do we use ‘at’ when we are talking about time? When do we ‘in’ when we are talking about time? What is the difference between ‘at night’ and ‘in the night’? What is the difference between ‘at the moment’ and ‘in a moment’? When do we use ‘on’ when we are talking about time?
 Genre/Topic: Prepositions
Genre/Topic: Prepositions
What is the difference between the prepositions ‘between’ and ‘among’? What does the phrase ‘among other things’ mean? Which is more preferable: ‘near’ or ‘close to’? Do ‘by’, ‘beside’ and ‘next to’ mean the same?
Download the complete course now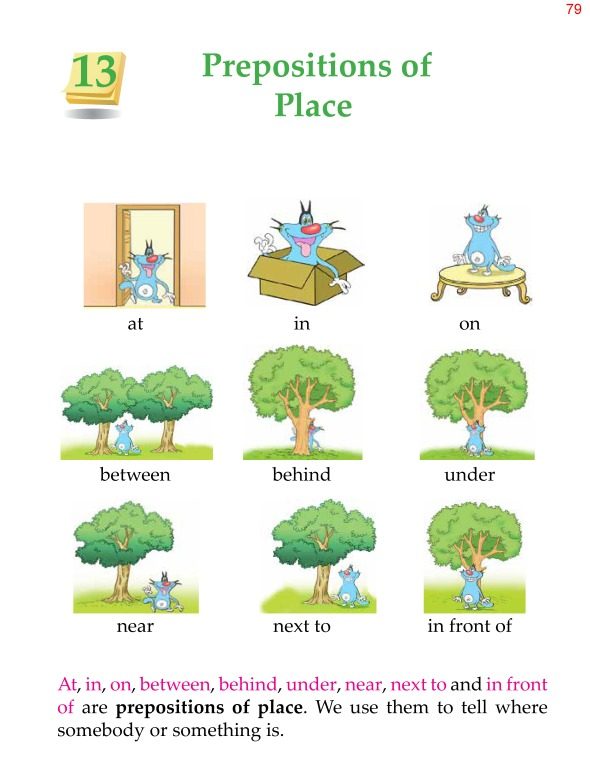 Genre/Topic: Parts of speech, Prepositions
Genre/Topic: Parts of speech, Prepositions
At, in, on, between, behind, under, near, next to and in front of are prepositions of place. We use them to tell where somebody or something is.
 Genre/Topic: Prepositions
Genre/Topic: Prepositions
What are prepositions? What are some prepositions of time? When do we use the preposition ‘at’? When do we use the preposition ‘on’? When do we use the preposition ‘in’? What is the difference between ‘on time’ and ‘in time’? What is the difference between ‘at the end’ and ‘in the end’? Do we also […]
 Genre/Topic: Prepositions
Genre/Topic: Prepositions
When do we use ‘during’? Can ‘during’ be substituted with ‘throughout’ or ‘over’? What is the difference between ‘for’, ‘by’ and ‘until’?
 Genre/Topic: Prepositions
Genre/Topic: Prepositions
What is the difference between ‘across’ and ‘over’? What is the difference between ‘along’ and ‘through’? What is the difference between ‘above’ and ‘over’? What is the opposite of above? What is the opposite of over? When are they used?
 Genre/Topic: Prepositions, Verbs
Genre/Topic: Prepositions, Verbs
What is the difference between ‘think of’ and ‘think about’? Which among the two, ‘think of’ or ‘think about’ is used to express intentions? What is the difference between ‘hear about’, ‘hear of’ and ‘hear from’? Do ‘laugh at’ and ‘laugh about’ mean the same thing?